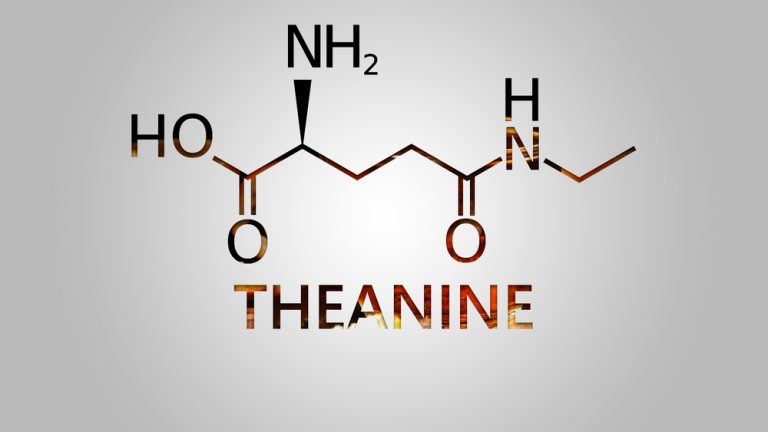
L-theanine is an amino acid commonly found in tea. Theanine, along with caffeine, produce a distinct profile of cognitive enhancement without nervousness and other side effects. In addition, theanine has many other surprising health benefits. Read this article to learn more about the health benefits that you can enjoy using theanine!
To start with Theanine
Theanine is the amino acid most commonly found in tea leaves and some fungi (1). This is used to improve mood and reduce stress levels and to protect the brain and heart. Theanine usually refers to L-theanine, which has more health benefits than D-theanine.

1. Theanine alleviate stress
After taking L-theanine, the subjects performed mental tasks. Compared with patients who took placebo, they had lower symptoms of stress with reduced blood pressure and blood pressure (2). Daily supplementation in patients with schizophrenia leads to a reduction in anxiety level (3). Theanine also promotes relaxation in healthy patients ( 4).
Additional doses of theanine, which promotes relaxation, do not cause sedation or dementia (5).
In addition, L-theanine may also act as a stimulant when administered at lower doses than those that promote relaxation (6).
2. It improves nervous system functions
L-theanine supplementation helps to increase attention and improve memory. In men and women who have had minor brain damage, the combination of L-theanine and green tea extract has increased the ability to remember during mental exercise. This was done by reducing the delayed recognition during the memory test (7).
During the memory test, the attention and alertness of the subjects was increased. An increased attention was also noted in healthy people who are susceptible to anxiety (8).
3. It helps in cardiovascular system prophylaxis
L-Theanine improves the function of blood vessels by increasing the production of nitric oxide (9). It also prevents the oxidation of LDL (low density lipoprotein) fat, which reduces the risk of arterial cure. Theanine also reduced blood pressure in hypertensive rats (10).
4. Theanine has enormous antioxidant effects
L-theanine in tea exerts antioxidant effects (11).
It also restores the antioxidant capacity of the liver cells, which prevents its injury (12). In rats, it reduced the oxidative damage and stopped inflammation (13).
5. It helps in mental illnesses
Taking 400 mg daily for eight weeks resulted in a reduced number of symptoms of schizophrenia. Patients reported lower levels of anxiety, less severe symptoms, and reduction of muscle problems (14).
6. It helps in losing fat!
Theanine, along with other components of green tea, reduce the concentration of triglycerides and fatty acids in the blood. In the mice treated with theanine, the intake of food and body weight decreased.
7. Support in cancer therapy
Theanine strengthens the effect of anticancer drugs (15). It also reduces the toxicity of these drugs to healthy tissues (16). Theanine reduces the growth and migration of cancer cells in the liver and lungs (17).
8. Theanine helps in depression state
In a recent open study, taking L-theanine for eight weeks helped to reduce depressive symptoms, anxiety, sleep disorders and cognitive impairment in patients with major depressive disorder (18).
9. Better sleep!
ADHD can cause sleep disorders. The boys who had been taking two 200-mg doses of L-Theanine over six weeks in six weeks had a higher sleep quality compared to those taking placebo (19).
They were less awake at night and easier to fall asleep.
10. Gastrointestinal prophylaxis
L-theanine heals stomach ulcers at a dose of 10 mg / kg, but exacerbates peptic ulcer disease if it is taken in a dose above 40 mg / kg.
Relieves the adverse effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as antioxidants and stimulates the production of prostaglandin E (20)
How does L-theanine work?
Theanine is able to cross the blood-brain barrier and affect the brain directly. In the brain, its action is directed to chemicals that regulate agitation, anxiety, pleasure and attention (21). When given to rats orally, theanine is in the blood after one hour and its peak in the brain after about five hours. It is completely eliminated and eliminated from the body within 24 hours (22).
L-theanine increases the levels of serotonin and dopamine in the brain. It affects the improvement of memory and learning abilities (23). It also increases levels as well as efficacy, GABA - the main inhibitory (inhibitory) neurotransmitter in the body (24). Theanine also increases the activity of the alpha brain wave, which causes relaxation, increases concentration and facilitates deep sleep REM (25). L-theanine increases the level of glutathione, the most important antioxidant molecule in the body.
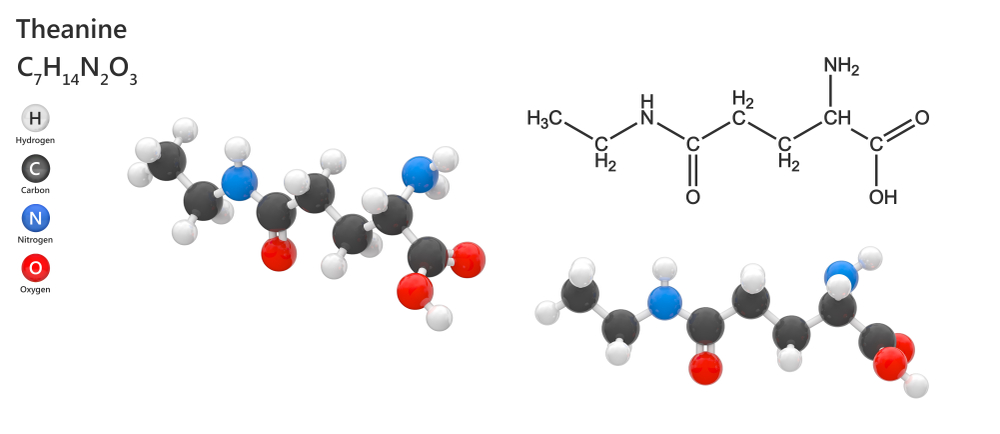
Test results with L-theanine
The kidneys preferentially absorbed and metabolized L-theanine. The kidneys secreted D-theanine (27) preferentially. Thus, independent of phosphate, kidney glutaminase hydrolyzed theanine (28). The increase in L - theanine was associated with decreased anxiety (P = 0.015, measured using the HARS scale) (29).
According to the 5-dimensional model of psychopathology, L-Theanine caused a significant reduction in the positive results of PANSS (P = .004) and the activation rate (P = .006) compared to placebo (30). The stratified random sampling showed that LGNC-07 improves memory and selective attention by significantly increasing the Rey-Kim memory quotient and reading words in people with MMSE-K 21-23 scores (LGNC-07, n = 11, placebo, n = 9 ) (31).
L-theanine increases the levels of serotonin, dopamine and GABA in the brain with possible improvement in memory and learning ability (32). Theanine exerts neuroprotective effects, probably by inactivating group 1 glutamate receptors in metabotrophy. L-theanine promotes the release of alpha waves associated with relaxation and mental concentration in young adults (33).
Natural sources of L-Theanine
- Tea leaves
- Japanese Camellia (green tea)
- Mushroom Bay Bolete
Side effects of L-theanine
In animal studies, oral L-theanine consumption did not cause toxic symptoms even at very high doses. However, when taking supplements, you should pay attention to the use of other drugs, especially those prescribed. Theanine can lower blood pressure. If you are taking medicines for blood pressure, it may be very low.
It can also reduce the effectiveness of stimulants. The appropriate dosage depends on the age and health of the user. A dose of 100 to 300 mg of theanine administered daily provides optimal health benefits and does not generate side effects.