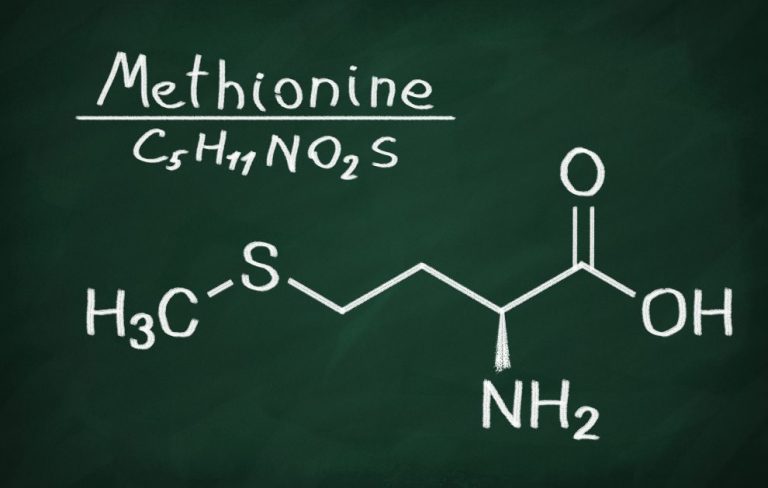
Methionine is an organic chemical compound belonging to the group of coded, exogenous amino acids, so it is not produced by the body, but must be delivered through diet or appropriate supplementation. It takes part in a large number of processes taking place in our body, which is why it is so essential for life. It is a sulfuric amino acid.
Methionine effect
The amino acid is extremely valuable in the body, without which many processes necessary for the proper functioning of the organism would not occur. Methionine takes part inter alia in the transformation of lipids, in the synthesis of choline, creatine and adrenaline, in the methylation cycle due to which glutathione has strong antioxidant properties. Methionine is a donor of methyl groups, it protects liver cells, it allows proper functioning of the nervous and muscular system. It has a very large impact on the beautiful appearance of hair, nails and skin. It is used in Parkinson's disease, in allergic diseases or in problems with the urinary and biliary system. Methionine is used for diabetes and atherosclerosis. It stimulates thinking and improving concentration.In the case of athletes, it works to increase physical efficiency.
Dosing of methionine
It is assumed that the demand for methionine in the form of supplements is 1-5 g / day twice a day.Of course, you can not forget about a proper diet, which is rich in meat, fish, eggs, cereal products, spinach, broccoli or beans. Its deficiency contributes, among other things, to raising blood cholesterol levels, to weakening hair and nails, lowering mood, to mental disorders and poorer immunity. Too large doses, in turn, can cause excess, which will be manifested, inter alia, headaches, drowsiness, constipation, acidification of the body or gastrointestinal disorders.
Studies confirming the effectiveness of methionine
Research by Klimer McCully confirmed that methionine works to treat atherosclerosis by destroying the lining of the arteries and other body cells.Research by Mauro G. Di Pasquale also showed a greater tendency to atherosclerosis, to increase cholesterol and to a higher lipid propensity for peroxidation.
It turns out that the functions that meet methionine in the body are, however, and much wider. It is she who is very important in removing unnecessary toxins and substances from the body and it strengthens the joint cartilage and causes its reconstruction, thus acting perfectly on the joints