Collagen - properties and action. How does it affect our health?

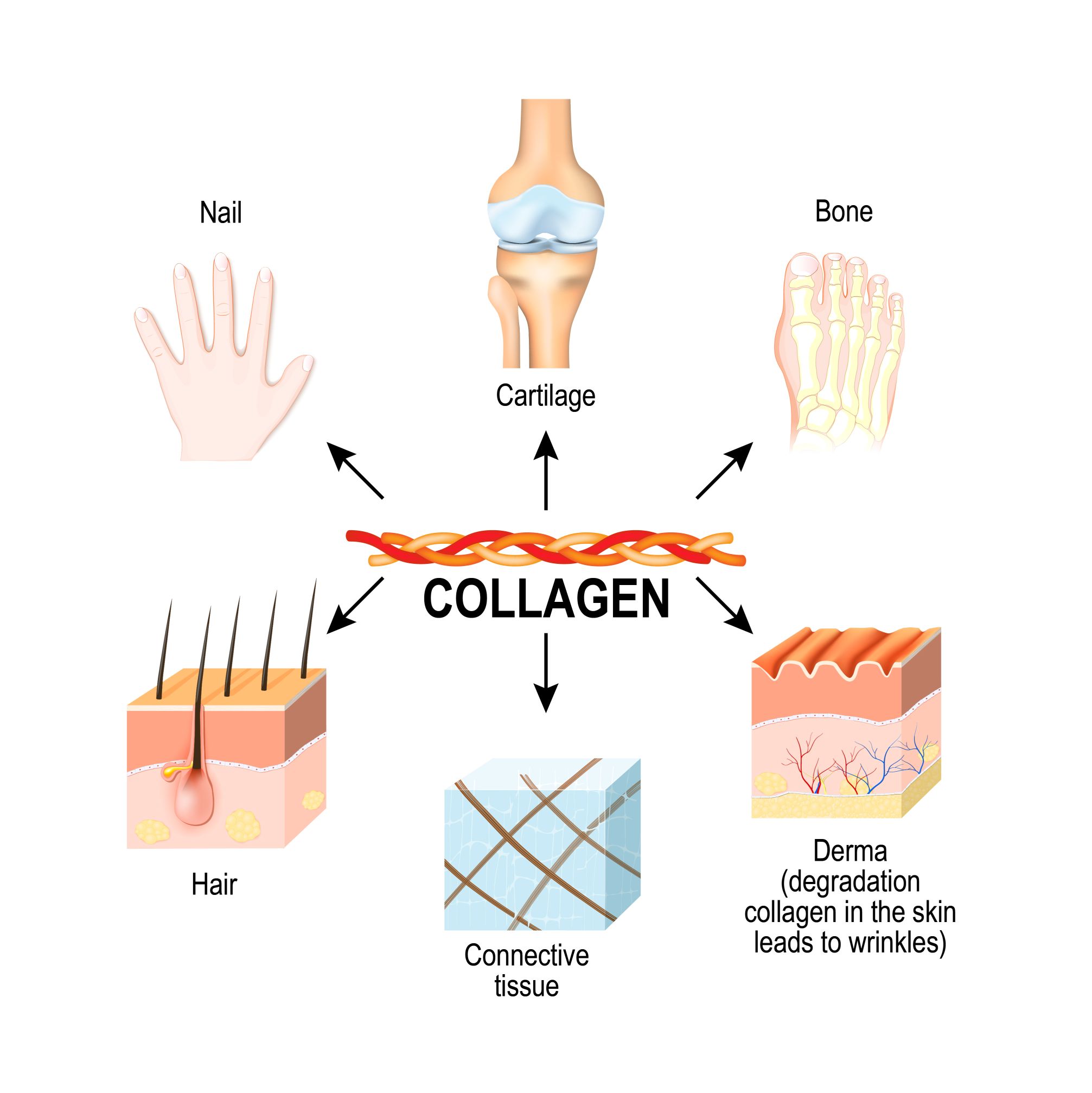
Collagen is a structural protein naturally found in the human body, in places such as skin, muscles, bones and tendons, for example. Interestingly, it accounts for one-third of the total amount of protein in humans and is thus the most abundant form of structural protein in the human body. Because it is a major component of the extracellular matrix, it is essential for the formation, strengthening and regulation of the function and regeneration of this tissue.
- What is collagen and what is it used for?
- Properties of collagen
- When is it best to take collagen?
- Is collagen healthy?
What is collagen and what is it used for?
Collagen is an essential component of connective tissue, and its primary role is to keep the connective tissue in good condition and the protective mechanical properties of the skin. It accounts for 65 to as much as 80% of the dry weight of the tendon, and collagen bonds help the tendon structure build resistance to intense stress and shear forces. For this reason, collagen plays an important role in maintaining tendon health and mitigating the potential risk of injury in sports. It is also worth mentioning that type II collagen is the main component of articular cartilage, which is responsible for the tensile strength of cartilage
Collagen is characterized by a high concentration of three amino acids - glycine, proline and hydroxyproline, which form its characteristic triple helix structure. As such, it undergoes enzymatic hydrolysis, resulting in its breakdown into smaller bioactive peptides that form the primary complementary form of collagen, which are readily absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract before finally entering the bloodstream. Thanks to hydrolysis, collagen peptides do not have the gelling properties of gelatin and are soluble in cold water. Among the richest sources of collagen peptides currently available on the dietary supplement market are hydrolyzed beef, pork, marine and poultry collagen.
Properties of collagen
Collagen strengthens blood vessels, improves the elasticity and hydration of the skin, increases the mechanical strength of bones and determines the normal structure of joint cartilage. It has been suggested that dietary supplementation with collagen preparations can alleviate inflammation, pain and joint swelling in osteoarthritis patients. In addition to reducing bothersome symptoms associated with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, it has beneficial effects on the condition of skin, hair and nails.
The results of a meta-analysis published in 2019, including 5 randomized clinical trials (RCTs), showed that taking collagen preparations contributed to a significant reduction in the severity of symptoms (especially joint stiffness) assessed using the WOMAC and VAS scales in osteoarthritis patients. It is also worth mentioning that there is evidence that three months of dietary supplementation with hydrolyzed collagen at a daily dose of 10 grams can surpass the effectiveness of glucosamine sulfate taken at 1,500 mg per day in terms of improving WOMAC and VAS scores in osteoarthritis patients. Initiating the repair process through the accumulation of collagen peptide in cartilage tissue helps maintain cartilage structure and function, with the positive consequences of alleviating pain and reducing the rate of articular cartilage degradation.
A recent systematic review of 15 RCTs with predominantly recreational athletes found that the use of hydrolyzed collagen had the most beneficial effect on improving joint function and reducing perceived joint pain. Some improvements in body composition, muscle strength and skeletal muscle recovery were also observed, particularly in older men with sarcopenia. It is worth mentioning that the rate of synthesis was most enhanced when taking hydrolyzed collagen at a dose of 15 g per day, although it did not have a significant effect on muscle protein synthesis (MPS), compared to whey protein.
When is it best to take collagen?
Based on the available literature, it is suggested that several months of dietary supplementation with hydrolyzed collagen at a daily dose in the range of 5 to 15 g contributes to a reduction in perceived joint pain and improved joint function, especially when used in conjunction with an appropriately selected strength exercise rehabilitation program. Current research shows that taking preparations containing its hydrolyzed form at a dose of 15 g per day was more effective in increasing collagen synthesis than 5 g per day. Hence, it is recommended to take hydrolyzed collagen at a dose of 15 g per day about 60 minutes before exercise to maximize synthesis and obtain the greatest health benefits from additional dietary supplementation....
Is collagen healthy?
Since the beneficial effects of taking hydrolyzed collagen usually appear only after three months or even longer, long-term adherence to the recommended supplementation is key to getting the desired results. Long-term use of hydrolyzed collagen is considered safe for human health, and participants in the studies conducted so far have not reported any adverse side effects, even with higher doses (i.e., 60 grams per day) or various forms of dietary supplements containing collagen.
Sources:
- Choi FD, Sung CT, Juhasz ML, et al: Oral Collagen Supplementation: A
Systematic Review of Dermatological Applications. J Drugs Dermatol.
2019 Jan 1;18(1):9-16. - García-Coronado JM, Martínez-Olvera L, Elizondo-Omaña RE, et al:
Effect of collagen supplementation on osteoarthritis symptoms: a
meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Int Orthop.
2019 Mar;43(3):531-538. - Khatri M, Naughton RJ, Clifford T, et al: The effects of collagen
peptide supplementation on body composition, collagen synthesis, and
recovery from joint injury and exercise: a systematic review. Amino
Acids. 2021 Oct;53(10):1493-1506. - de Miranda RB, Weimer P, Rossi RC.: Effects of hydrolyzed collagen
supplementation on skin aging: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Int J Dermatol. 2021 Dec;60(12):1449-1461. - Wang H.: A Review of the Effects of Collagen Treatment in Clinical
Studies. Polymers (Basel). 2021 Nov 9;13(22):3868.
 ⮜ Previous article
⮜ Previous article
Best supplements for sleep. Learn about the most effective suggestions
 Next article ⮞
Next article ⮞