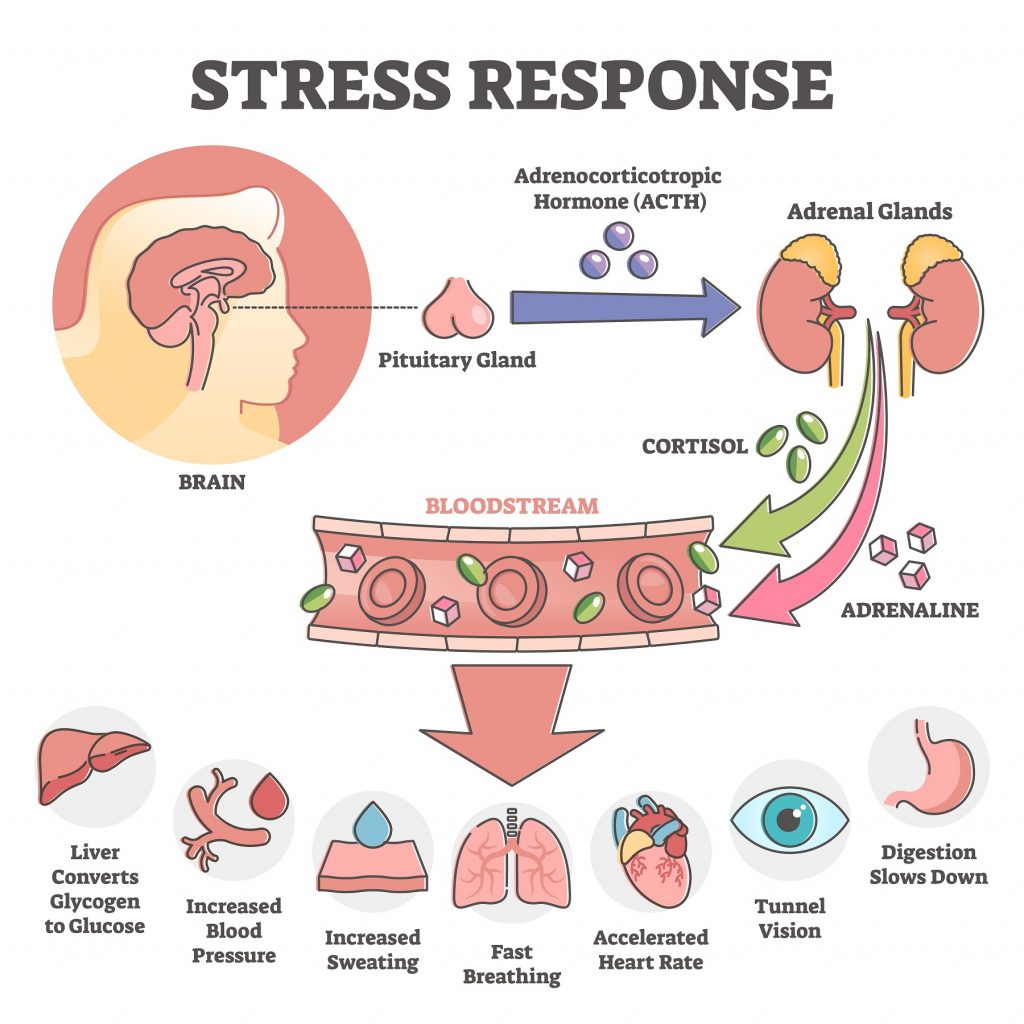
Cortisol, or hydrocortisone, is a glucocorticosteroid hormone produced in the adrenal glands, specifically through the striatal layer of the adrenal cortex. The synthesis and secretion of cortisol are under the control of corticotropin or adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), produced by the pituitary gland. In turn, the generation of ACTH is dependent on hypothalamic corticoliberin (CRH). This regulation is carried out on the basis of negative feedback. This means that an increase in ACTH leads to an increase in cortisol secretion. In turn, a significant increase in blood cortisol concentration implies a decrease in ACTH secretion. Thanks to this process, the correct internal homeostasis of the body is maintained.
What is cortisol?
Cortisol is one of the so-called stress hormones. In stressful situations, it is produced in larger quantities and contributes to increased blood glucose levels, because then the body requires more energy to function optimally during the stress.
Cortisol is often referred to as the stress hormone. This is, because in stressful situations its concentration increases, which stimulates the body to act in so-called “fight or flight response”. In this situation, among other things, the sugar level increases, respiratory rate increases, and blood pressure rises. However, if we are exposed to stress for a long period of time, our system synthesis much more cortisol than it should. In this case, the issue becomes quite troublesome, because high levels of this hormone persist not only in the morning but for the whole day, even in the evening. Consequently, cortisol becomes our enemy. Cortisol also develops the action of other stress hormones - adrenaline and noradrenaline, and thus supports the body in coping with the so-called stressor.
It is also worth noting that cortisol has an effect on
- protein metabolism, because it increases the breakdown of proteins,
- water and electrolyte balance, because it inhibits sodium in the body while increasing potassium excretion
- has an anti-inflammatory effect (relieves inflammation and allergies)
- weakens the immune system
- raises blood pressure,
- increased gastric secretion
- carbohydrate metabolism because it increases glycogenesis and gluconeogenesis,
- fat metabolism by increasing lipolysis
- calcium release from bones.
We must remember that excess cortisol has a negative effect on our bodies.
Cortisol should be considered mainly its correct concentrations’ ranges in mind.
The rules of normal serum cortisol level depending on the phase of the day are as follows:
- In the morning - from 138 to 690 nmol/l (5-25 µg/dl)
- At night - values half as high
It is worth taking care of appropriate and tested supplements. Our store offers you a range of products that will help in the fight against cortisol. In some cases, music therapy has also been shown to help reduce cortisol levels.
In order to avoid increased cortisol levels, we need to know what leads to increased cortisol levels.
These include
- Viral diseases
- Overuse of stimulants like caffeine
- Lack of sleep
- Melatonin supplementation increases cortisol levels in postmenopausal women
- Severe trauma or stressful situations
- Anorexia nervosa can be linked to increased cortisol levels
- The serotonin 5-HTR2C receptor gene in men is correlated with increased cortisol production.
- Inhalation of androstadienone by women
When analyzing all of the above factors, it is important to consider the possibilities that today's supplements offer us in the fight against cortisol.









