All about taurine
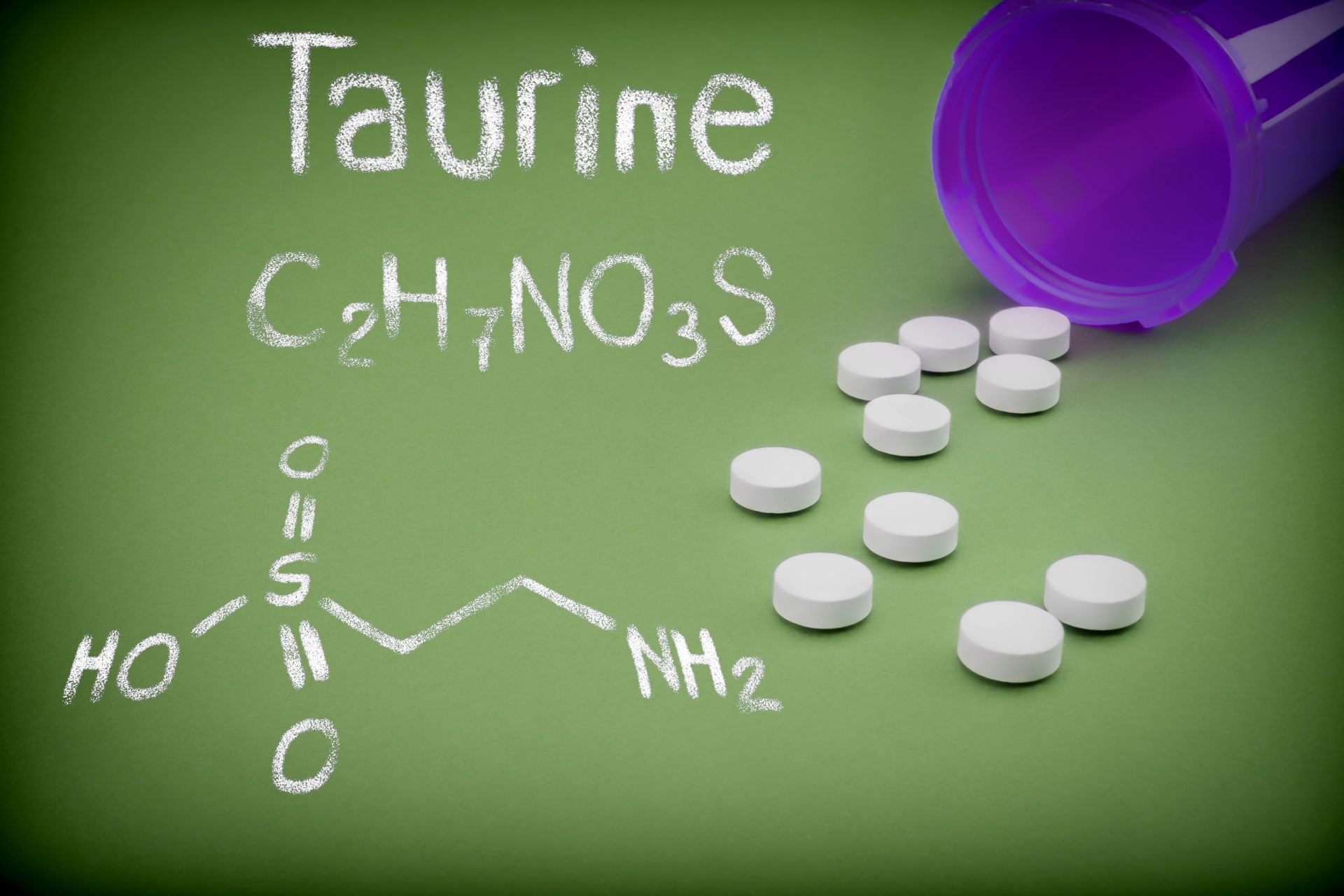
Taurine is a non-protein amino acid that is commonly found in the tissues of the human body. The largest amounts of taurine are found in the heart muscle and retina, and slightly smaller amounts in the brain, intestines, kidneys and skeletal muscle. Taurine is a compound that performs many different functions in the human body and can exhibit a wide range of health-promoting properties.
- Taurine - properties
- Taurine - dietary sources
- Taurine - dosage
- Taurine deficiency
- Taurine supplementation - is it safe?
Taurine - properties
Taurine is essential for the proper functioning of the cardiovascular system, as well as the development and functional activity of the brain, retina and skeletal muscles. Taurine participates in the production of bile acids, supports the body's antioxidant defense system, stabilizes cell membranes and reduces inflammation. In addition, taurine influences energy metabolism, blood glucose and lipid concentrations, and regulates calcium and sodium ion levels in cells. Taurine has been shown to exhibit antioxidant, ergogenic (increasing exercise capacity in regular athletes), antihypertensive, and hepato- and neuroprotective properties.
Current studies show that taurine supplementation at doses of 1.5 to 6.0 grams per day can contribute to a significant reduction in systolic and diastolic blood pressure values, by an average of 3 mmHg. Moreover, the use of taurine at a dose of 0.5 to 6.0 g per day for a period of 2 weeks to 6 months can effectively reduce systolic and diastolic blood pressure and blood total cholesterol and triglyceride levels in patients with metabolic disorders (including: diabetes, hepatitis, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, obesity, cystic fibrosis, chronic alcoholism). There are also indications that a three-month supplementation of taurine in a daily dose of 6 g (3 times a day, 2 g each) can reduce the activity of liver enzymes, namely AspAT and ALT in patients with chronic hepatitis. Little, the results of a study involving women aged 33-54 showed that one-month taurine supplementation at a daily dose of 3 g can lead to a reduction in blood homocysteine levels.
It also proved that taurine supplementation at doses of 1.0 to 6.0 g per day can increase muscle endurance during endurance exercise. It has been suggested that taurine supplementation may improve not only aerobic capacity, but also anaerobic capacity (muscle strength and power) and post-exercise recovery (reduce DOMS), and may lead to a decrease in selected markers of skeletal muscle damage (e.g., creatine kinase - CK).
Taurine - dietary sources
It is estimated that the average adult consumes between 40 and 400 mg of taurine each day, depending on the amount of animal products in the diet. Taurine is mainly found in foods of animal origin, such as meat, offal, fish and seafood. Among the richest dietary sources of taurine are:
-
Oysters - 396 mg/100 g,
-
Atlantic salmon - 130 mg/100 g,
-
Pork liver - 89 mg/100 g,
-
Beef liver - 69 mg/100 g,
-
Tuna - 68 mg/100 g,
-
Pork - 61 mg/100 g,
-
Lamb - 44 mg/100 g,
-
Beef - 43 mg/100 g,
-
Veal - 40 mg/100 g,
-
Cod - 31 mg/100 g.
Taurine is also found in energy drinks at a level of 350-400 mg in 100 ml of the drink. In addition, the human body has the ability to produce taurine at a level of 50 to 125 mg per day. Taurine is synthesized in the liver and brain with the help of sulfur amino acids (methionine and cysteine) and vitamin B6.
Taurine - dosage
Based on the available scientific evidence, it is indicated that the optimal taurine dosage for measurable health benefits should range from 1.5 to 6.0 g per day. To lower systolic and diastolic blood pressure values, it is most often recommended to take 1.5 g of taurine daily, which should be divided into three smaller portions of 0.5 g each. On the other hand, to improve physical performance during endurance exercise, 1 to 3 g of taurine should be taken 60-120 minutes before the start of exercise to achieve maximum bioavailability.

Taurine deficiency
Chronic deficiency of taurine in the human diet can lead to central nervous system dysfunction (e.g., depression, anxiety disorders, psychomotor hyperactivity), degenerative changes in the retina, impaired liver function and cardiovascular dysfunction**. Deficiency of taurine in the human body can be caused by low intake of animal products, which are naturally abundant in taurine. Hence, vegans and vegetarians are particularly vulnerable to taurine deficiency, as they do not provide taurine to the body with food at all. In addition, taurine deficiency can result from an abnormal supply of vitamin B6 and methionine, chronic use of antiepileptic drugs (especially vigabatrin) and long-term supplementation with high doses of beta-alanine, which blocks the action of taurine.
Taurine supplementation - is it safe?
Studies have shown that taurine supplement ation in daily doses ranging from 0.5 to as much as 10 grams has no adverse health effects. It is suggested that long-term taurine supplementation at a dose of 3 g per day is completely safe for human health and carries no risk of any adverse effects. Taurine has very low toxicity, and the established average lethal dose (LD-50) for rats is as high as over 7 g per kg of total body weight.
Sources:
-
Kurtz JA, VanDusseldorp TA, Doyle JA, et al: Taurine in sports and exercise. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2021 May 26;18(1):39.
-
Schaffer S, Kim HW: Effects and Mechanisms of Taurine as a Therapeutic Agent. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2018 May 1;26(3):225-241.
-
Jong CJ, Sandal P, Schaffer SW.: The Role of Taurine in Mitochondria Health: More Than Just an Antioxidant. Molecules. 2021 Aug 13;26(16):4913.
-
Bae M, Ahmed K, Yim JE: Beneficial Effects of Taurine on Metabolic Parameters in Animals and Humans. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2022 Jun 30;31(2):134-146.
-
Guan L, Miao P.: The effects of taurine supplementation on obesity, blood pressure and lipid profile: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020 Oct 15;885:173533.
-
Waldron M, Patterson SD, Tallent J, et al: The Effects of an Oral Taurine Dose and Supplementation Period on Endurance Exercise Performance in Humans: A Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2018 May;48(5):1247-1253.
 ⮜ Previous article
⮜ Previous article
When is the best time to exercise? - Training in the morning or evening
 Next article ⮞
Next article ⮞