B12 is one of the most important vitamins circulating in our body. It is worth mentioning, however, that vitamin B12 is not a single substance and it is present in several forms, including cyanocobalamin, methylcobalamine, hydroxocobalamin and adenosylcobalamin, which show some differences. Let's look at the properties of each of these products in order to be able to personalize and maximize its benefits.
Definition of vitamin B12 and its role in the body
Cobalamin is a water-soluble vitamin with a very complex structure in which the central atom is cobalt, which is also indicated by its name. It participates in hematopoietic processes, and its deficiency is one of the factors causing anaemia. The neurological role of this vitamin is well known. It participates in the production of myelin sheaths on neurons, in the synthesis of neurotransmitters that affect our mood, in the synthesis of DNA molecules, and in the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates and lipids.
The role of the methylation cycle and the dysfunction within it is mentioned more and more. Methylation is the process of transferring the methyl molecule from one molecule to another. A common disorder in this cycle is excessive accumulation of homocysteine in the bloodstream. B12 supports one of its pathways to methionine, which can then be re-used by the body. Specifically, it’s about supporting the action of the methionine synthase enzyme, which attaches the methyl group taken from methyltetrahydrofolate to homocysteine to form methionine. Methionine is then formed by SAMe (s-adenosylmethionine), which is the most important donor of methyl groups and conditions the course of many biochemical processes.
The main factors influencing the possibility of vitamin deficiency are:
- Vegan and vegetarian diets, because this vitamin is typically a zoonotic and we will not find its active forms in plants
- Old age, which is the cause of frequent cognitive and neurodegenerative disorders
- Disorders involving absorption and / or digestion
- Use of proton pump inhibitors or metformin
To help you choose the right B12 supplement for you, let's investigate what each of these forms means.
Cyanocobalamin
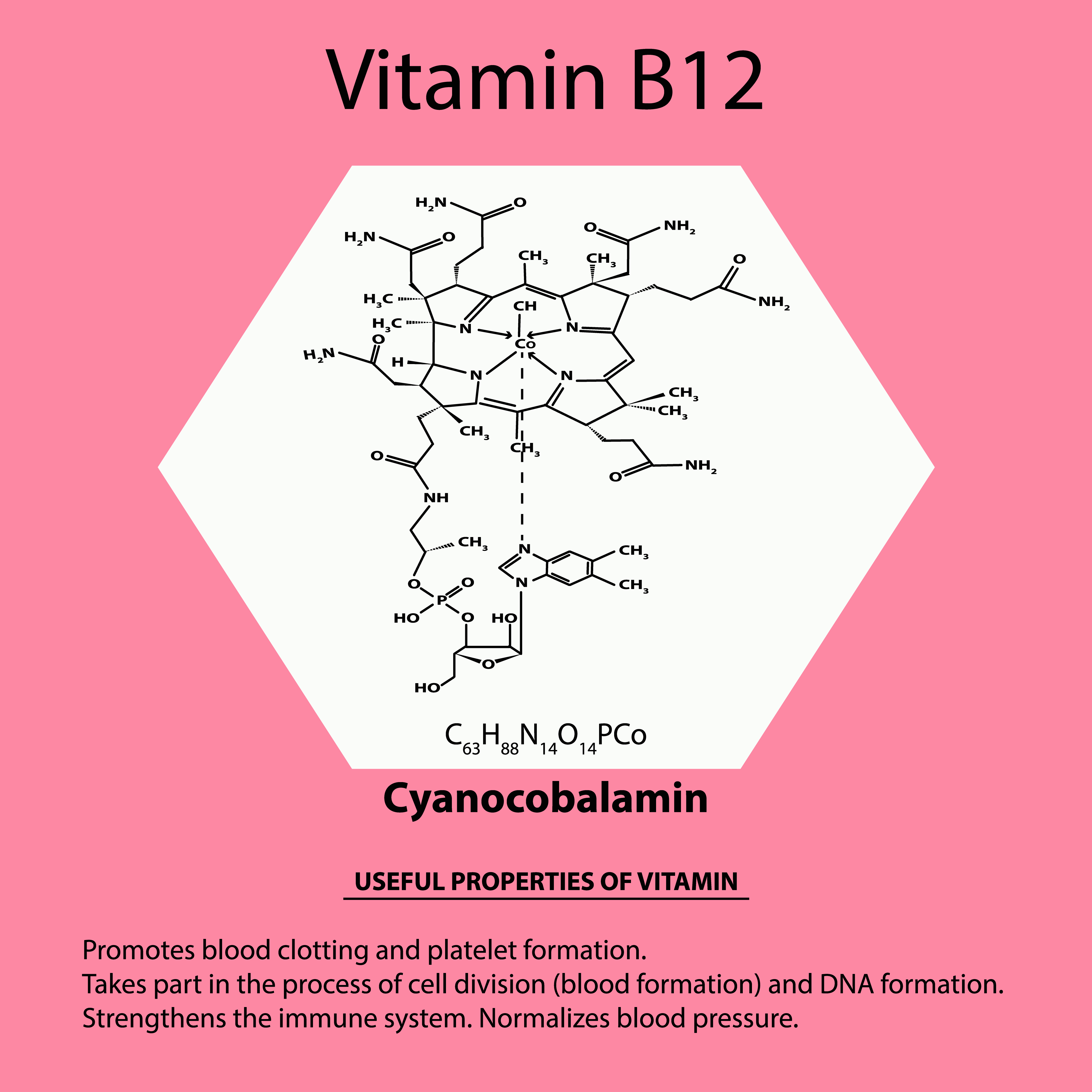
The most common, cheapest form of B12. Unfortunately, despite being widely used in many supplements, it’s not an optimal choice. Potentially harmful is the presence of cyanide, which is a strong toxin. True, it is not found in significant amounts, but even small amounts of it must involve some processes responsible for detoxification to remove cyanide from the body. Interestingly, vitamin B12 is involved in the removal of cyanide. Just after delivering this form into our body, part of the vitamin must be immediately consumed.
Methylcobalamin
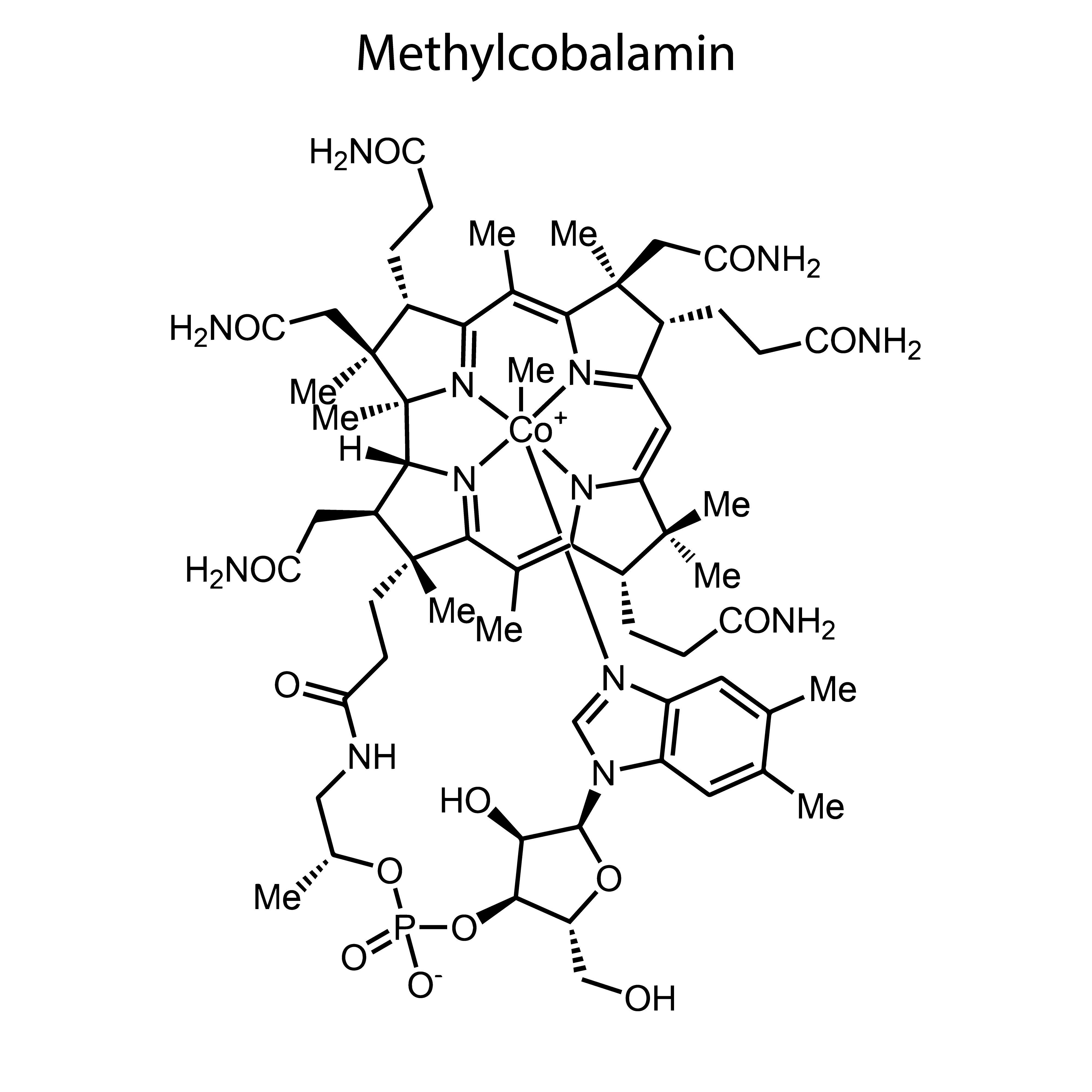
This form has in recent years won the hearts of many people who are serious about the selection of the right supplements. Unlike cyanocobalamin, it does not deliver toxins and is immediately active, ready for use by cobalamin-dependent enzymes. It is precisely to the cyanocobalamin that cyanocobalamin is converted after the cyanide is removed.
Methyl cobalamin additionally provides methyl groups which can be used in many reactions. The commonality of disorders in the already mentioned methylation cycle often results in the need to provide more methyl groups, and in such cases the supplementation with the methylated version yields very favourable, clearly noticeable effects.
Methylated B12 may have analgesic effect in diabetic neuropathy, lower back pain and in various types of neuralgia. This effect is due to the regenerative properties of neurons and the potency of noradrenaline and serotonin, which can reduce the pain. Scientific data show that the full therapeutic effect is only achieved after the addition of adenosylcobalamin to the methylated version, but methyl-B12 has a stronger effect on blood production than adenosyl-B12. This form of regular supplementation protects the neurons from the excitotoxicity induced by excessive stimulation of the NMDA receptors by glutamate. Methyl cobalamin is an important contributor to folate when we set about lowering homocysteine levels in the blood. There are also indications of its suitability in the treatment of certain androgen-dependent androgen-dependent malignancies.
Hydroxocobalamin
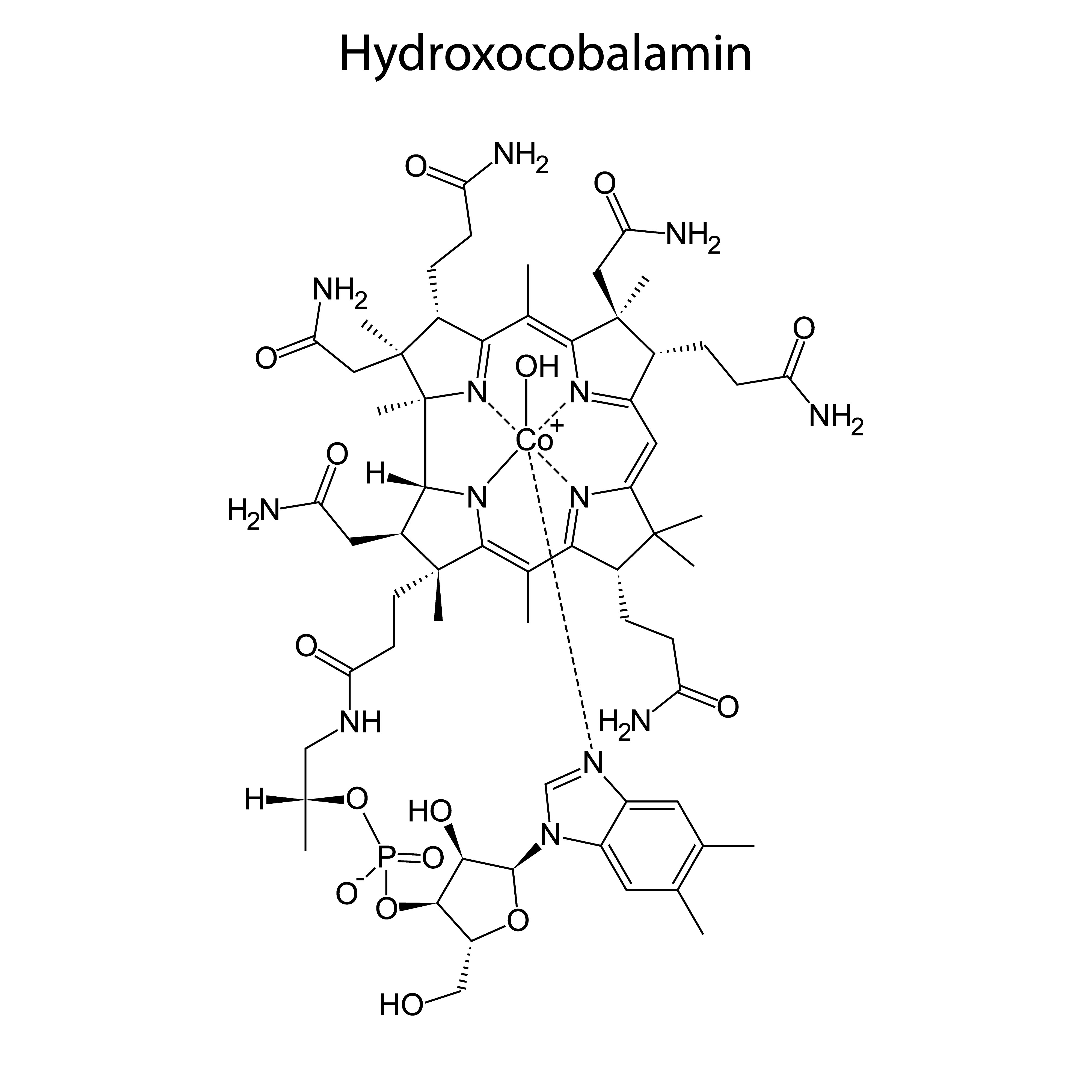
This form of B12 will appeal to those who have a problem with an excess of methyl groups in the body (what is called over-methylation), where pre-methylated form of cobalamin can cause potential problems, including mood disorders.
Hydroxocobalamin is very efficiently converted to methylcobalamin and adenosylcobalamin, which are active forms used by the body. This allows us to benefit from the methylated form, but without smuggling further methyl groups into the organism, which would unduly increase their total potency. It’s recommended especially for those who do not feel well when supplementing with methylcobalamin, and want to take a supplement of better quality than cyanocobalamin.
This form of vitamin B12 is an effective antidote to very dangerous cyanide poisoning that can even lead to death. It can also help fight tobacco addition, neutralizing cyanide smuggled in with smoke. By comparing hydroxyl to cyanocobalamin, the former exhibits greater efficacy in the treatment of vitamin B12 deficiency through better retention in the body, improved transport to cells, and more effective conversion to coenzymatic active forms. The hydroxyl form is more effective than cyano-lowering levels of methylmalonic acid and homocysteine in people with cobalamin metabolism disorders. Hydroxy- and adenosylborabalamines are the most abundant forms of vitamin B12 in food. The hydroxyform is the one that maintains the high blood B12 concentration for the longest time.
Adenosylcobalamin
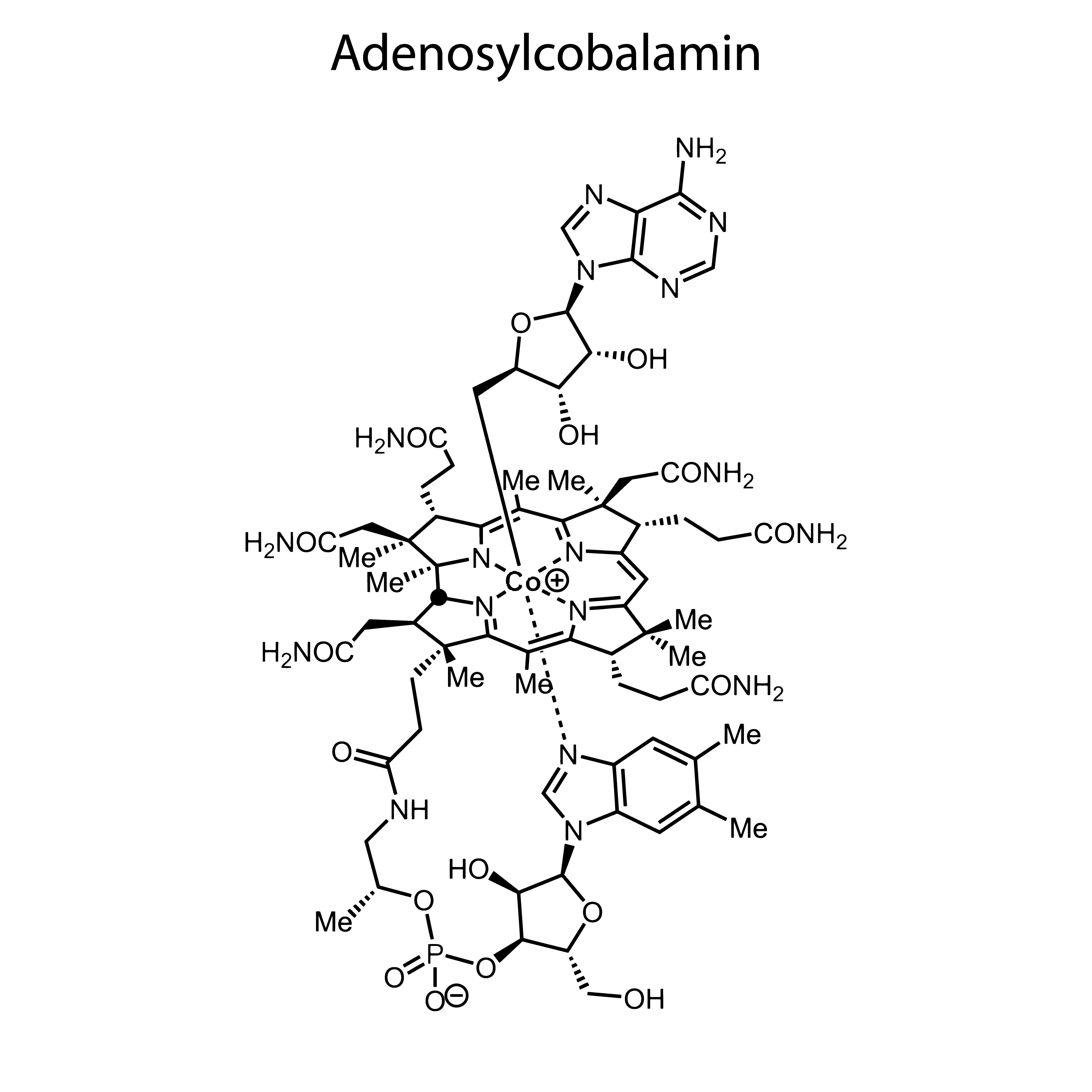
Cobalamin with 5-deoxyadenosine molecule attached. Next to hydroxy-B12 is the most abundant form of this vitamin in food. This form is known as mitochondrial B12. This is another active form that does not require conversion to begin with, but unlike methylcobalamin it does not provide additional methyl groups to the body. It acts as a cofactor for the methylmalonyl coenzyme A muta- tion enzyme, which converts methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA, thereby supporting energy metabolism.
It’s indicated that it’s adenosylcobalamin which has the effect of regenerating myelin sheaths. It also participates in the leucine synthesis process.
Summary
Undoubtedly vitamin B12 plays a huge role in the human body, but the choice of its form when deciding on supplementation is also of great importance. The popularity of methylcobalamin in the place of cyanocobalamin has been clearly shown in recent years, which is a very good trend. However, to achieve the full benefits, it’s recommended to use methyl and adenosylcobalamin combination.
It must be borne in mind, however, that not all respondents respond well to the supply of methyl groups, including methylcobalamin. In this situation, the best solution is to use hydroxocobalamin alone or in combination with adenosylcobalamin.









